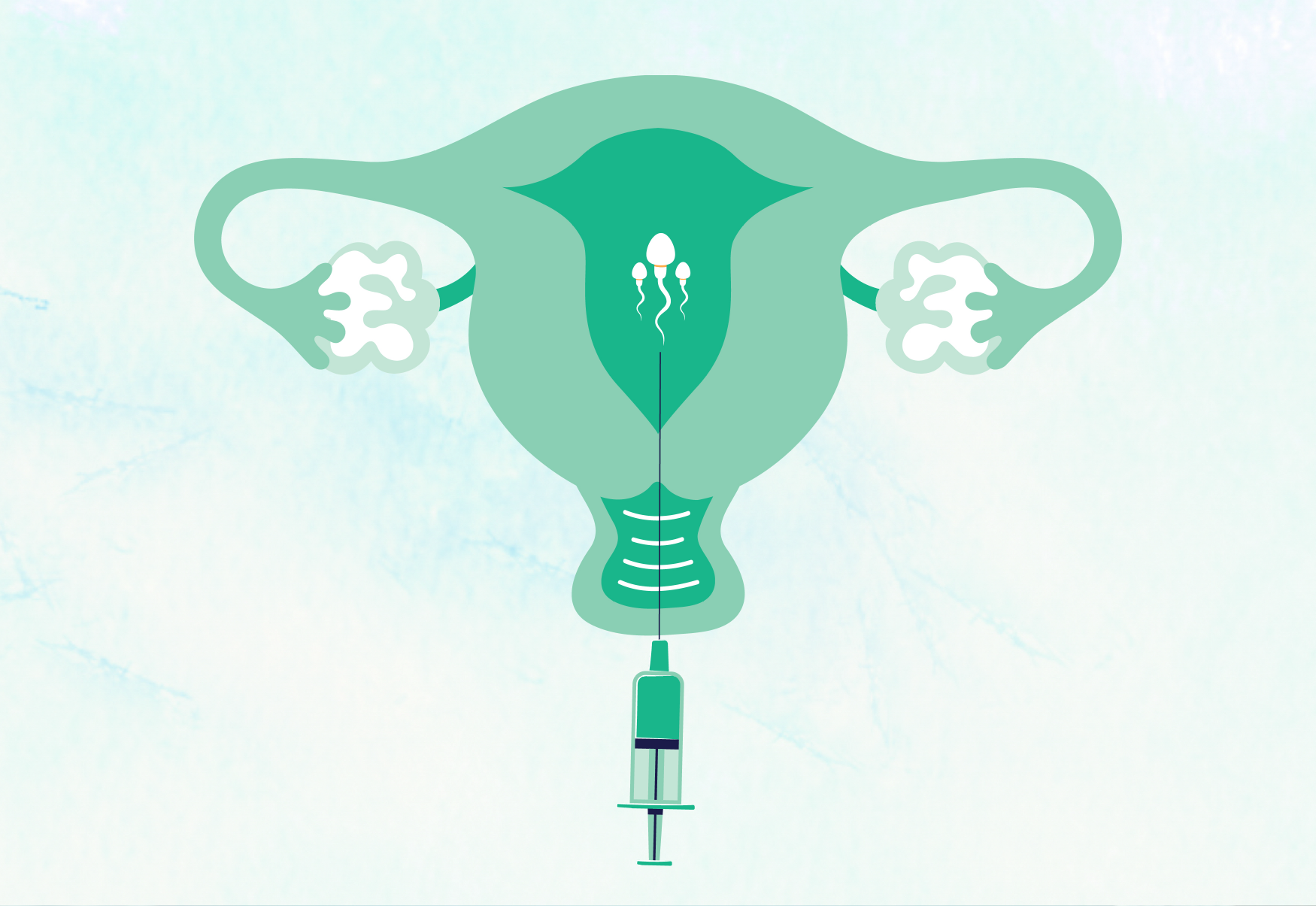
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) involves injecting a sample of sperm directly into the uterus using a small plastic tube. The tube is threaded through the cervix and the sperm is injected during or around the time of ovulation. This method involves preparing the sperm sample by selecting only live and motile sperm and injecting them into the uterus without the need for the sperm to swim through the cervix. This allows a large number of motile sperm to enter the uterus and be ready to fertilize the egg. Therefore, IUI is often performed for couples experiencing unexplained infertility, where the male partner has below-standard sperm quality or issues related to sperm delivery into the cervix, or if the female partner has issues such as endometriosis or problems with ovulation. However, it is not suitable in cases where there is blockage of both fallopian tubes or severely compromised sperm quality.
Preparation for the female partner:
The physician will stimulate the ovaries to promote the growth of follicles during a specific menstrual cycle. This is typically done using injectable or oral medications, which are often started on the third day of the menstrual cycle. Afterward, an appointment will be scheduled for an ultrasound examination to monitor the size and number of follicles, as well as the thickness of the endometrial lining. When the follicles reach an appropriate size, the physician will administer medication to trigger ovulation. Approximately 36-40 hours after the trigger medication, ovulation will occur. Another appointment will be scheduled for the administration of the sperm insemination, which involves injecting prepared sperm into the uterine cavity on the day of ovulation. The patient will need to meet with the physician only three times during this process.
Preparation for the male partner:
The male partner must meet with the physician on the scheduled day for IUI procedure and abstain from sexual intercourse for 2-7 days in order to collect the semen sample. The semen sample should be delivered within one hour. Subsequently, a specialized scientist will perform a screening and select only viable and motile sperm for the physician to inject into the uterine cavity. This preparation process will take approximately 1-2 hours.
IUI Procedure
Once the sperm sample is prepared, it is placed in a small plastic tube free from contaminants. The physician will gently insert this small tube through the cervix. Afterward, the physician will inject the sperm into the uterine cavity, and the procedure takes only a few minutes. It is painless, and after undergoing IUI, you can resume your normal activities without the need to stay at the clinic.
What to do after IUI:
- After the sperm injection, you will be advised to rest for approximately 30 minutes before leaving the clinic.
- Refrain from sexual intercourse on the day of the IUI, but afterward, you can resume sexual activity as usual.
- Maintain a healthy diet, get enough rest, and engage in regular physical activity.
- The physician will schedule a follow-up appointment for pregnancy testing approximately two weeks after the sperm injection.
The success rate of Intrauterine insemination (IUI) depends on several factors. Generally, the success rate of triggering ovulation and performing IUI is between 10-20% per treatment cycle, based on studies conducted on individuals with unexplained infertility. It has been found that the chances of pregnancy with IUI are approximately twice as high as natural conception. However, if IUI is combined with ovulation induction medication taken orally, the chances increase to about three times. If ovulation is induced with injectable medication, the chances increase to 4-6 times compared to natural conception.
- The age of the female partner.
- The number of mature eggs available for fertilization.
- The concentration of the sperm used for injection into the uterine cavity and the thickness of the uterine lining on the day of insemination.
However, the physician will carefully control these factors to optimize the chances of pregnancy. IUI is a widely used assisted reproductive technique that offers a reasonable success rate, is safe, and is cost-effective. However, if IUI is not successful, the physician may consider utilizing other assisted reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) for further treatment.