In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a procedure performed outside the body to achieve pregnancy. It involves retrieving mature eggs from the female partner and combining them with healthy and motile sperm from the male partner in a laboratory dish. This is done under suitable temperature and humidity conditions to facilitate fertilization and the subsequent development of embryos. After fertilization occurs externally, the resulting embryos are transferred back into the uterus to establish a pregnancy.
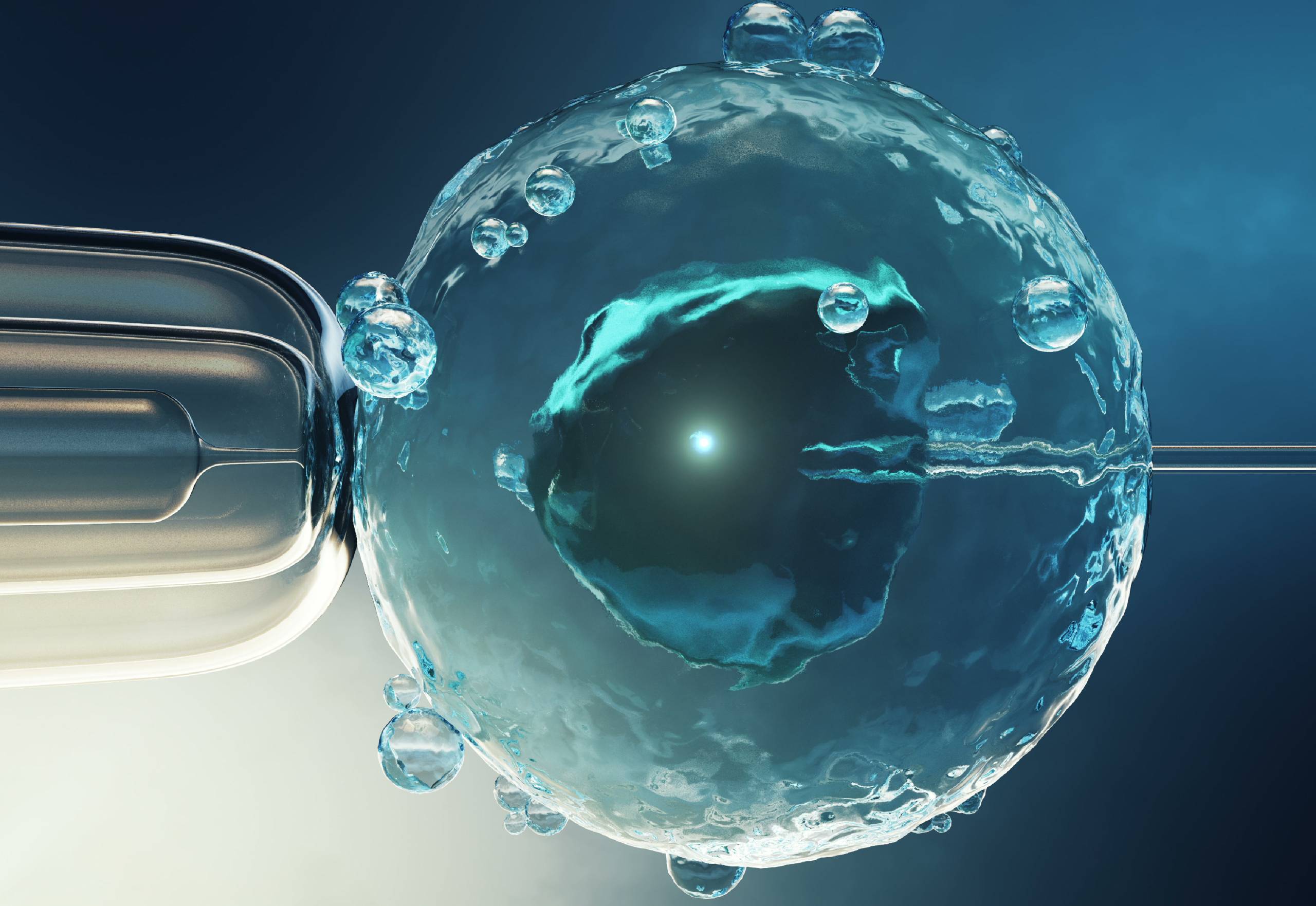
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) differs from IVF in terms of the fertilization process. In ICSI, a single mature egg and a single healthy sperm are selected and directly injected into the egg using a micro-needle. This ensures fertilization and the development of an embryo. The resulting embryo is then transferred back into the uterus to establish a pregnancy. ICSI is particularly useful in cases where the male partner has a low sperm count or significant abnormalities in sperm motility.
Therefore, the main difference between these two methods is that ICSI is a highly targeted fertilization technique, whereas IVF allows natural fertilization to occur. ICSI increases the chances of success when dealing with male factor infertility or issues with sperm quality. It enables the selection of the most viable sperm for fertilization. Consequently, ICSI is more commonly used than conventional IVF in such cases.
IVF and ICSI are effective fertility treatments; however, it is crucial to seek accurate guidance from a specialist physician and adequately prepare both the male and female partners for the IVF and ICSI procedures.
Who is suitable for IVF?
- Couples in which the female partner has blocked or damaged fallopian tubes on both sides.
- Couples in which the male partner has issues related to sperm, such as low sperm count or poor sperm motility.
- Couples who have been trying to conceive for more than one year without success and have unexplained infertility.
- Couples who have previously undergone intrauterine insemination (IUI) but have not achieved pregnancy.
- Couples with unexplained infertility, where the cause of the difficulty in conceiving is unknown.
- Women who have been diagnosed with endometriosis.
Preparation before treatment:
- Both the female and male partners should have a balanced diet supplemented with appropriate vitamins.
- Sufficient rest is important, aiming for at least 8 hours of sleep per day.
- Regular exercise should be incorporated.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption should be avoided to enhance the body’s hormonal response to treatment.
- Follow the instructions provided by the physician.